How Do Solar Panels Work? A Simple Guide to Solar Power
If you’ve ever looked up at a rooftop covered in shiny panels and wondered, “How do solar panels work?”—you’re not alone. Solar panels have become popular for homeowners and businesses with the growing push toward renewable energy and eco-conscious living. But despite their widespread adoption, the science behind these sun-catching devices remains a mystery to many.
We at Mianro Solar believe that homeowners deserve to be energy-independent and live without fear of the next utility bill. But did you know just how powerful and cost-effective solar energy has become?
This guide’ll explain how solar panels generate electricity, what components are involved, and why they’re a smart investment for a greener future.
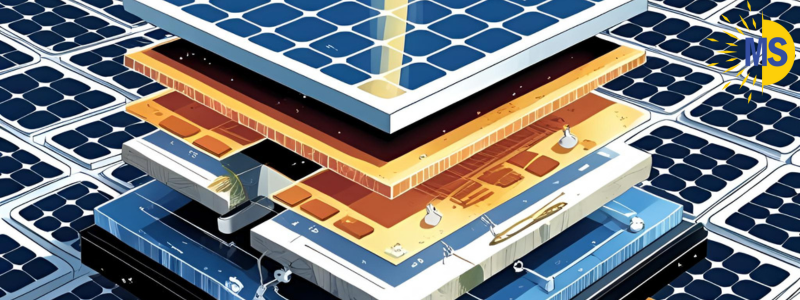
What Are Solar Panels Made Of?
At the core of a solar panel is the photovoltaic (PV) cell, a small semiconductor device typically made from silicon. These cells are the engines of the panel, converting sunlight into usable electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect.
A typical panel consists of:
- Multiple PV cells arranged in a grid
- A glass casing for protection
- An insulation layer and a back sheet to prevent moisture and overheating
An anti-reflective coating to absorb more sunlight
Together, these components form an efficient system that harnesses the sun’s rays and turns them into clean power.
So, How Do Solar Panels Work?
Let’s simplify the science.
Sunlight Hits the Solar Panel
The process begins when photons (tiny packets of solar energy) hit the solar panel’s surface. These photons carry enough energy to dislodge electrons from the atoms inside the PV cells.
The Photovoltaic Effect Takes Place
When photons strike the semiconducting material (usually silicon), they create an electrical field across the layers of the cell. This field causes the freed electrons to move—this flow is what we call electric current.
DC Electricity is Generated
The electrons flow in one direction, producing direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter Converts DC to AC Power
Most homes and appliances use alternating current (AC) electricity. So the DC power from the panels must be passed through an inverter, which converts it into AC power you can use.
Power is Delivered to Your Home
Once converted, the electricity flows to your home’s breaker box, powering everything from lights to your refrigerator.
Excess Energy is Stored or Sent Back to the Grid
If your system generates more energy than you use, the surplus can be stored in batteries or exported to the grid (if net metering is available in your area), earning you credits on your electric bill.
Did you know?
The amount of sunlight that hits the Earth in just 90 minutes could power the world’s total energy needs for an entire year!
Solar Power By the Numbers
- 25+ years: The average lifespan of a modern solar panel.
- Up to 70% savings: Homeowners can cut their electricity bills by up to 70% after switching to solar.
- 2 million+ homes: Over 2 million U.S. homes now use solar panels, and the number is growing fast!
- Zero emissions: Solar energy is 100% renewable and helps reduce your carbon footprint- one typical home solar system offsets about 3-4 tons of CO₂ per year.
Understanding the Key Components of a Solar System

Besides the panels and inverter, a solar power system includes several supporting parts to ensure optimal performance.
- Solar Panels: Made up of many solar cells, responsible for converting sunlight into electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC to AC.
- Battery (Optional): Stores excess energy for use during the night or cloudy days.
- Mounting System: Secures panels to your roof or ground-based structure.
- Performance Monitor: Tracks electricity production in real-time.
Types of Solar Panel Technology

Not all solar panels are created equal. Here are the most common types used in homes and businesses:
1. Monocrystalline Panels
- Made from a single crystal of silicon
- High efficiency (15–22%)
- Longer lifespan and sleek appearance
- Slightly more expensive
2. Polycrystalline Panels
- Made from multiple silicon fragments
- Lower cost but slightly less efficient (13–16%)
- More blue-tinted appearance
3. Thin-Film Panels
- Lightweight and flexible
- Less efficient but ideal for large-scale projects with ample space
- Shorter lifespan
Each type has its pros and cons, depending on your budget, roof space, and energy goals.
Solar PV vs. Solar Thermal: What’s the Difference?
While both technologies harness the power of the sun, they serve different purposes:
- Solar PV (Photovoltaic): Converts sunlight into electricity. This is the technology used in standard solar panels.
- Solar Thermal: Uses sunlight to heat water or air. Common in solar water heaters and some industrial applications.
Do Solar Panels Work on Cloudy Days or at Night?
Yes—but with limitations.
- On Cloudy Days: Solar panels still generate electricity, just at a reduced rate (10–25% of their normal output, depending on the panel quality and cloud density).
- At Night: No electricity is generated, which is where batteries or a grid connection come in handy.
How Efficient Are Solar Panels?
Modern solar panels typically operate at 15–22% efficiency, depending on the type and conditions. While that might not sound like much, it’s more than enough to power an average household when scaled properly.
Several factors affect solar panel performance, including:
- Angle and direction of installation
- Shading from trees or buildings
- Temperature (panels work better in cooler conditions)
- Panel type and brand
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
One of the biggest reasons people go solar? It’s clean, renewable, and sustainable. Here’s what makes solar power a win for the planet:
- Zero greenhouse gas emissions during energy production
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels
- Low water usage compared to coal or nuclear power plants
- Minimal operating costs after installation
Every kilowatt-hour (kWh) of solar power used can offset more than 1 pound of carbon dioxide that would have been generated from fossil fuels.
Real-World Applications: How Solar Powers America
From residential rooftops to massive solar farms, the U.S. is steadily increasing its renewable energy portfolio. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar power has the potential to provide up to 40% of the nation’s electricity by 2035.
Common applications include:
- Homes and apartments
- Businesses and commercial buildings
- Schools and universities
- Utility-scale solar farms
- Electric vehicle charging stations
Common Questions About Solar Panels
How long do solar panels last?
Most panels come with a 25–30-year warranty, but they often continue producing power beyond that with slightly reduced efficiency.
What is the average cost of installing solar?
The Average cost of solar depends upon your location and system size, U.S. homeowners typically pay $15,000–$25,000 after tax incentives.
Can I go completely off-grid?
Yes, but you’ll need a battery storage system and a large enough array to cover your energy needs 24/7.
Is solar power worth it?
Absolutely—especially if you live in a sunny state. With federal tax credits, state incentives, and net metering, solar can pay for itself in as little as 6–8 years.
The Future of Solar Power
Solar technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace. Researchers are exploring:
- Perovskite solar cells for higher efficiency
- Solar skins that blend with roof tiles
- Solar windows and transparent panels
- Floating solar farms for space efficiency
These innovations could make solar even more affordable and accessible soon.
Why Go Solar Now?
- Electricity rates are rising: U.S. residential electricity prices have increased by over 15% in the past five years.
- Solar incentives: Federal and state incentives can cover up to 30% of installation costs.
- Increase home value: Homes with solar panels sell for up to 4% more than those without.
Summary
To sum it all up, solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. They generate DC electricity, which is converted into AC power through an inverter and then used to run your home. Solar energy is not only clean and renewable—it’s also a smart way to lower your energy bills and reduce your carbon footprint.
America continues its transition toward renewable energy, solar power stands out as a reliable, cost-effective, and planet-friendly solution.
So the next time you see a rooftop solar array, you’ll know exactly what’s happening behind those shiny panels.
Ready to Take Control of Your Energy?
Imagine never worrying about high utility bills again! Find out how much you could save by switching to solar. Our experts at Mianro Solar are ready to help you become energy independent.
Interested in Solar?
Call 844-464-0003 or email us at info@mianrosolar.com for a savings analysis today!
Take the first step toward a brighter, cleaner, and more affordable future. Contact us now and let’s power your home with the sun!